樹突狀細胞
2011年的諾貝爾生醫獎得主史坦曼,發現樹突狀細胞(DC)是人類免疫細胞系統的司令官,號令主導免疫系統的各種功能。DC的功能是吞噬、加工及呈遞抗原,將交手過的癌細胞特征告訴輔助T細胞和B細胞。接受樹突DC細胞指令的輔助T細胞,會活化細胞毒性T細胞、自然殺手NK細胞、巨噬細胞和已經接受樹突DC細胞刺激的B細胞;細胞毒性T細胞會在辨識癌細胞后予以毒殺,少數的細胞毒性T細胞會被輔助T細胞轉為記憶T細胞;自然殺手NK細胞會直接攻擊癌細胞,巨噬細胞則會更容易分解所吞噬的癌細胞。
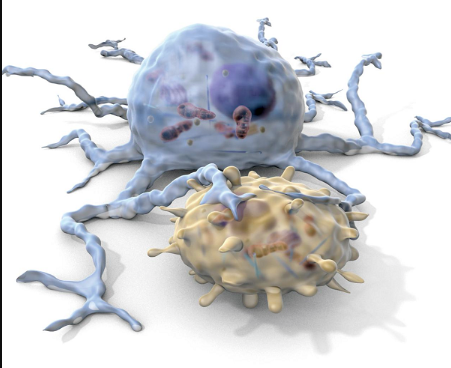
Fig.1 A dendritic cell (blue) engages a T cell (yellow).
DC作為目前公認的最有效的抗原呈遞細胞,在介導固有免疫應答和誘導適應性免疫應答中起關鍵作用,可以誘導腫瘤免疫耐受。基于DC的免疫療法是利用患者自身免疫系統的潛力消除轉移性、難治性惡性腫瘤中的腫瘤細胞。許多DC疫苗已進行了臨床測試,且具有免疫原性,在某些情況下與臨床結果相關。以DC為基礎的腫瘤免疫治療相關的臨床研究在國內外不斷開展,體現了腫瘤免疫治療在惡性腫瘤治療中的強大優勢。
DC屬于單核吞噬細胞(mononuclear phagocytes ,MPs),MPs包含巨噬細胞,單核細胞,樹突狀細胞。樹突狀細胞(DC)的亞群具有不同的發育特征,專門用于啟動不同類型的效應T細胞,從而調整免疫反應的結果。最初,樹突狀細胞被分為淋巴和髓系兩類,但這一命名方法并不能準確反映每個樹突狀細胞亞群的發育起源。按照來源和分化途徑可以將樹突狀細胞分為傳統DCs(conventional DCs,cDCs),血漿DCs(plasmacytoid DCs,pDCs),朗格漢斯細胞(Langerhans cells,LCs)。cDCs又分為傳統I型樹突狀細胞(cDC1)和傳統II型樹突狀細胞(cDC2)。
Fig. 2 Functionally specialized conventional and non-conventional dendritic cell subsets and related lineages.
cDC1
cDC1起源于CD34+造血干細胞,分化過程受包括干擾素調節因子8 (IRF8)在內的轉錄因子組合的調節;具有獨特的C型凝集素受體CLEC9A和趨化因子XCR1的表達特征。cDC1通常被稱為交叉呈遞DCs,因其具有交叉呈遞抗原的能力,并能夠引起腫瘤免疫反應。
Fig. 3 Illustration depicts the common signatures and shared signatures expressed by human and mouse conventional dendritic cell subset 1. The signature includes surface markers, transcription factors and major pattern recognition receptors. The signatures with * marks indicate tissue specific expression.
cDC2
cDC2是通過高水平表達MHC II、CD11c和SIRPA來識別的。cDC2亞群主要依賴于IRF4和Zeb2介導的轉錄調控,而cdc1依賴于IRF8、BATF3和ID2。cDC2是存在于人體不同組織和器官中主要的DC群體,它們表達一系列TLRs,能夠對從核苷酸到多糖的各種危險信號作出反應。與其他穩態DC亞群相比,它們還表達了高水平的NLRPs和其他炎癥相關信號分子,表明它們具有感知不同危險信號的功能。
Fig. 4 Illustration depicts the common signatures and shared signatures expressed by human and mouse conventional dendritic cell subset 2. The signature includes surface markers, transcription factors and major pattern recognition receptors. The signatures with * marks indicate tissue specific expression.
pDCs
當遇到病毒感染細胞時,pDCs被確定為產生干擾素的細胞亞群,它們產生I型干擾素和激活效應細胞的能力在啟動抗病毒免疫應答方面具有關鍵作用。pDCs對許多RNA和DNA病毒有響應,包括VSVG, HCV, HAV, LCMV,登革熱病毒等。
Fig. 5 Illustration depicts the common signatures and shared signatures expressed by human and mouse plasmacytoid dendritic cell. The signature includes surface markers, transcription factors and major pattern recognition receptors.
LCs
LCs最早于19世紀被Paul Langerhans發現,后來被認為是DC細胞的一個亞系。歷史上,LCs被認為是樹突狀細胞,因為它們具有典型的樹突狀細胞遷移到淋巴結、呈遞抗原和激活T細胞的特征。LCs位置優越,位于外界環境的最外部,是免疫系統的第一道防線。
Fig. 6 Specialized functions of mouse classical dendritic cell subsets.
基于已有研究,人類和小鼠DC已經被成功分成不同功能的亞群。構建遺傳小鼠模型,通過檢測表面標記物不同組織的表達情況,有助于功能冗余的亞群統一。同樣的,這些模型有助于分離具有非冗余功能的表型相似的亞群。對于人類DC的研究,也已經沿著這些思路取得了進展。
[1]Anderson D A , Dutertre C A , Ginhoux F , et al. Genetic models of human and mouse dendritic cell development and function[J]. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2020.
[2]Eisenbarth S C . Dendritic cell subsets in T cell programming: location dictates function[J]. Nature reviews. Immunology, 2018, 19(2).
[3]Balan S , Saxena M , Bhardwaj N . Dendritic cell subsets and locations[J]. International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology, 2019.
[4]Mueller,K. L . A dendritic cell target for immunotherapy[J]. Science, 2014, 346(6209):597-597.
[5]Steinman, Ralph M . Decisions About Dendritic Cells: Past, Present, and Future[J]. Annual Review of Immunology, 2012, 30(1):1-22.
[6]Broz M L , Binnewies M , Boldajipour B , et al. Dissecting the Tumor Myeloid Compartment Reveals Rare Activating Antigen-Presenting Cells Critical for T Cell Immunity[J]. Cancer Cell, 2014, 26(5):638-652.




 17312606166
17312606166